24++ Why Does Current Decrease When Voltage Increases In A Transformer Information
Why does current decrease when voltage increases in a transformer. So if a step-down transformer decreases voltage it increases current. They only convert it into different forms. To summarize the answer is the current is lower when the voltage is higher due to conservation of power and the voltage increases in direct proportion to the number of times the secondary output wire is wrapped around the transformer magnetic core secondary windings to the number of primary windings. That secondary current will result in a primary current transformer ratio again. Inductance is directly proportional to the inductive reactance and frequency. If resistor exists resistance decreases according to ohms law current is directly proportional to voltage and current is inversely proportional to resistance it means as current increases. So we position a step-up transformer at the source end of the line which increases voltage and decreases current and then we position a step-down transformer at the load end of the line which reduces the voltage to manageable and safe levels and boosts current. The PFers told me that the transformers increase the current available. A device called a transformer boosts the voltage while cutting current in the same proportion. The voltage is increased from about 25000 Volts V to. L f and L XL. Decreasing voltage increases current In the National Grid a step-up transformer is used to increase the voltage and reduce the current.
If it cuts the voltage output in half the current output doubles. Secondary current flow through the secondary winding resistance causes another voltage drop hence lower transformer output voltage. So the turns ratio doesnt cause a lower or higher current in the load. Under load both the primary and secondary winding resistance contribute to a lower secondary voltage. Why does current decrease when voltage increases in a transformer If I have a 1200 watt 120 volt heater it will draw 10 amps. It has no moving parts and works on a magnetic induction principle. The AC voltage is stepped up or down using transformers and transformers pass power voltage times current not voltage or current. I think I understand it now. That secondary voltage will cause a certain current to flow through the load I VR. Voltage of a transformer at a given flux density increases with frequency and also decreases with it. The current does not flow unless there is a load. A transformer converts alternating current AC from one voltage to another voltage. Voltage across the primary of a transformer creates a magnetic field whose flux creates a corresponding voltage in the secondary by Faradays Law of Induction.
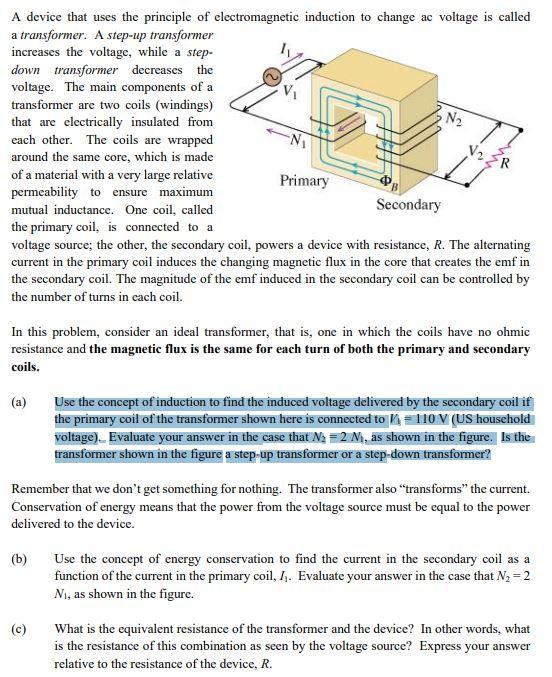
Why does current decrease when voltage increases in a transformer When transformers decrease the voltage the transformers increase the current that is available if a circuit is formed.

Why does current decrease when voltage increases in a transformer. Which states that the voltage is. In a step down transformer voltage gets decreased and current capability increases. This causes a secondary voltage transformer ratio.
If the power companys lodal distribution voltage is 12000 volts they will use a 1001 step-down tranformer to deliver 120 volts to me. Now Say a transformer is designed for 50 Hz frequency but if the frequency becomes high or low what would happen. Step-down transformers never create or loser power.
In a step up transformer we all know voltage increases and current decreases the answer to more voltage is because it has more windings but why does more windings induce more voltage cant the Stack Exchange Network. When resistance increases the circuit current decreases and vice versa. So a step up transformer increases the voltage and a step down transformer decreases the voltage.
Before a circuit is formed there is no current. We can get this from Transformer universal emf equation. You apply your supply volts to the primary.
As we already know that in a step-up transformer if voltage increases the current decreases where power is same as transformer only step-up or step-down the value of current and voltage and doesnt change the value of power. It can be designed to step-up or step-down voltage. Inductive reactance is a kind of resistance.
Heres my current theory. So that the output signal now has double the current capability as the input signal. If transformer efficiency is close to 1 then output product.
The voltage of a transformer has a proportional relationship with frequency. The secondary winding resistance does.
Why does current decrease when voltage increases in a transformer The secondary winding resistance does.
Why does current decrease when voltage increases in a transformer. The voltage of a transformer has a proportional relationship with frequency. If transformer efficiency is close to 1 then output product. So that the output signal now has double the current capability as the input signal. Heres my current theory. Inductive reactance is a kind of resistance. It can be designed to step-up or step-down voltage. As we already know that in a step-up transformer if voltage increases the current decreases where power is same as transformer only step-up or step-down the value of current and voltage and doesnt change the value of power. You apply your supply volts to the primary. We can get this from Transformer universal emf equation. Before a circuit is formed there is no current. So a step up transformer increases the voltage and a step down transformer decreases the voltage.
When resistance increases the circuit current decreases and vice versa. In a step up transformer we all know voltage increases and current decreases the answer to more voltage is because it has more windings but why does more windings induce more voltage cant the Stack Exchange Network. Why does current decrease when voltage increases in a transformer Step-down transformers never create or loser power. Now Say a transformer is designed for 50 Hz frequency but if the frequency becomes high or low what would happen. If the power companys lodal distribution voltage is 12000 volts they will use a 1001 step-down tranformer to deliver 120 volts to me. This causes a secondary voltage transformer ratio. In a step down transformer voltage gets decreased and current capability increases. Which states that the voltage is.
Indeed lately is being hunted by consumers around us, maybe one of you personally. People now are accustomed to using the net in gadgets to see image and video data for inspiration, and according to the name of this article I will talk about about Why Does Current Decrease When Voltage Increases In A Transformer.
Why does current decrease when voltage increases in a transformer. The voltage of a transformer has a proportional relationship with frequency. The secondary winding resistance does. The voltage of a transformer has a proportional relationship with frequency. The secondary winding resistance does.
If you re searching for Why Does Current Decrease When Voltage Increases In A Transformer you've reached the right location. We have 51 graphics about why does current decrease when voltage increases in a transformer adding images, photos, pictures, wallpapers, and more. In these web page, we also have variety of images out there. Such as png, jpg, animated gifs, pic art, symbol, black and white, transparent, etc.